
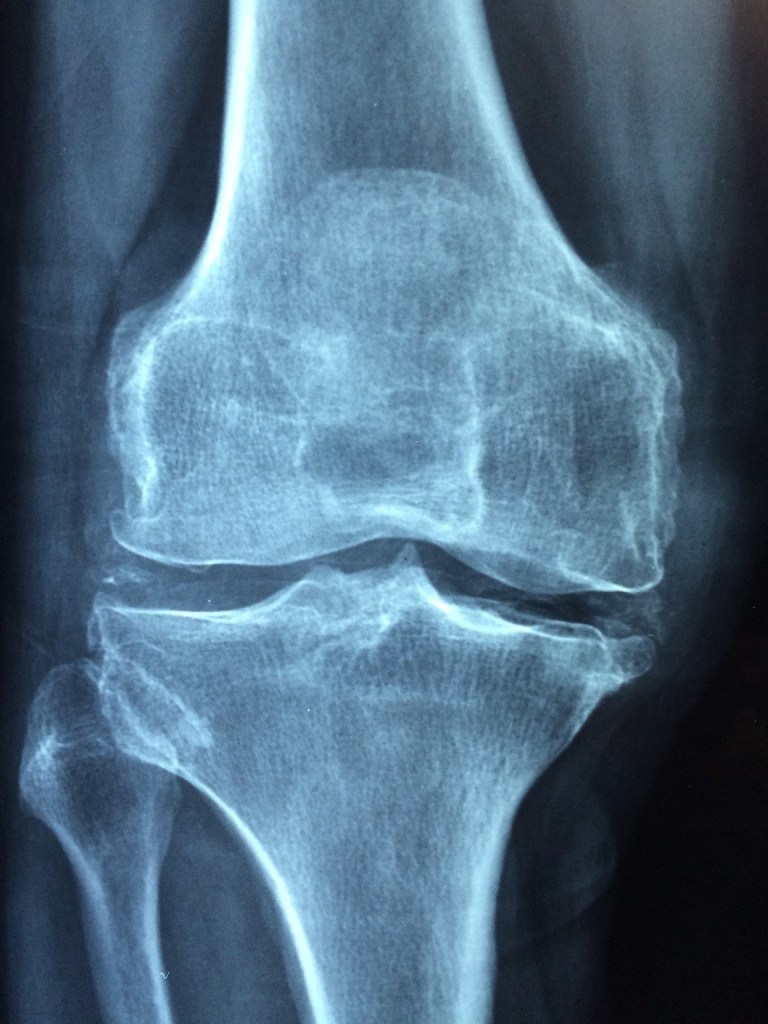
Osteoarthritis (OA) is a degenerative joint disease characterized by the breakdown of cartilage, leading to pain, stiffness, and decreased mobility. It is particularly common in weight-bearing joints such as the knees, affecting millions of people worldwide. While it can impact both sexes, the prevalence tends to increase with age. Managing osteoarthritis involves a combination of lifestyle changes, medical treatments, and sometimes surgical interventions. This article delves into the various approaches to treating knee osteoarthritis.Causes and SymptomsOsteoarthritis of the knee occurs when the cartilage that cushions the ends of the bones in the joint deteriorates over time. The primary causes include aging, obesity, joint injuries, repetitive stress on the joint, genetics, and certain metabolic diseases. Symptoms typically develop gradually and may include:Pain: The most common symptom, which worsens with activity.Stiffness: Particularly noticeable after periods of inactivity.Swelling: Caused by inflammation in the joint.Loss of flexibility: Difficulty in moving the joint through its full range of motion.Grating sensation: A feeling of bone rubbing on bone.Lifestyle ModificationsWeight ManagementMaintaining a healthy weight is crucial for managing knee osteoarthritis. Excess weight puts additional stress on the knee joints, exacerbating pain and accelerating cartilage breakdown. Weight loss through a combination of diet and exercise can significantly reduce symptoms and improve joint function.Physical ActivityRegular, low-impact exercise helps strengthen the muscles around the knee, improving stability and reducing pain. Recommended activities include:Walking: Gentle on the joints and can be easily incorporated into daily routines.Swimming and water aerobics: The buoyancy of water reduces stress on the knees while allowing a full range of motion.Cycling: Strengthens the quadriceps muscles without putting undue stress on the knees.Strength training: Focus on building the muscles around the knee to provide better joint support.Medical TreatmentsMedicationsSeveral medications can help manage the symptoms of knee osteoarthritis:Pain relievers: Over-the-counter options like acetaminophen can help with mild pain.Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs): Ibuprofen and naproxen can reduce pain and inflammation.Topical treatments: Creams and gels containing NSAIDs or capsaicin can be applied directly to the skin over the knee.Corticosteroid injections: These can provide temporary relief from severe pain and inflammation.Hyaluronic acid injections: These may help lubricate the knee joint, providing pain relief for some people.Physical TherapyWorking with a physical therapist can be highly beneficial. They can design a personalized exercise program to strengthen the muscles around the knee, improve flexibility, and enhance overall joint function. Additionally, physical therapists can teach patients how to use assistive devices like braces, canes, or shoe inserts to reduce stress on the knee.Alternative and Complementary TherapiesHerbal Remedies and SupplementsSeveral natural and herbal remedies have shown promise in managing osteoarthritis symptoms:Glucosamine and chondroitin: These supplements are thought to support cartilage health and reduce pain.Turmeric: Contains curcumin, which has anti-inflammatory properties.Ginger: Known for its anti-inflammatory and analgesic effects.Boswellia: An herbal extract with anti-inflammatory properties.Omega-3 fatty acids: Found in fish oil, these can help reduce inflammation.AcupunctureAcupuncture, a traditional Chinese medicine technique, involves inserting thin needles into specific points on the body. Some studies suggest it can help reduce pain and improve function in people with knee osteoarthritis.Massage TherapyMassage can help alleviate muscle tension, improve circulation, and reduce pain. Techniques such as Swedish massage, deep tissue massage, and myofascial release may be beneficial.Surgical InterventionsWhen conservative treatments fail to provide adequate relief, surgical options may be considered:ArthroscopyThis minimally invasive procedure involves inserting a small camera into the knee joint to repair or remove damaged tissue. However, its effectiveness for osteoarthritis is debated, and it is generally not recommended as a first-line treatment.OsteotomyThis procedure involves cutting and reshaping the bones to relieve pressure on the knee joint. It is typically recommended for younger patients with knee osteoarthritis who are not ready for a knee replacement.Joint Replacement SurgeryTotal or partial knee replacement involves removing the damaged joint surfaces and replacing them with artificial components. This is usually considered when other treatments have failed, and the patient’s quality of life is significantly impacted by pain and limited mobility.Pain Management TechniquesHot and Cold TherapyApplying heat or cold to the knee can help reduce pain and inflammation. Heat therapy can relax muscles and improve circulation, while cold therapy can numb the area and reduce swelling.Transcutaneous Electrical Nerve Stimulation (TENS)TENS uses low-voltage electrical currents to relieve pain. Small electrodes are placed around the knee, and the electrical impulses can help block pain signals to the brain.Preventive MeasuresProtecting the JointsAvoid high-impact activities: These can cause further joint damage. Opt for low-impact exercises instead.Use proper footwear: Supportive shoes can help reduce stress on the knees.Modify activities: Make changes to daily activities to avoid overloading the knee joints.Staying InformedEducation: Understanding the condition and staying informed about treatment options can empower patients to make better decisions regarding their care.Regular check-ups: Regular visits to healthcare providers can help monitor the progression of osteoarthritis and adjust treatment plans as necessary.ConclusionOsteoarthritis of the knee is a chronic condition that requires a comprehensive approach to manage effectively. By combining lifestyle modifications, medical treatments, alternative therapies, and, if necessary, surgical interventions, individuals with knee osteoarthritis can achieve significant relief from symptoms and improve their quality of life. It’s important for patients to work closely with their healthcare providers to develop a personalized treatment plan that addresses their specific needs and goals. Regular monitoring and adjustments to the treatment plan can help ensure the best possible outcomes.


Leave a Reply to Pequeño mundo (pk🌎) Cancel reply